אנו משתמשים בקובצי עוגיות באתר שלנו. בהמשך השימוש באתר, אתם מסכימים לשימוש שלנו בקובצי עוגיות. למידע נוסף, עיינו במדיניות הפרטיות שלנו.
שתלים דנטליים מהווים פתרון חדשני לשיקום שיניים חסרות.
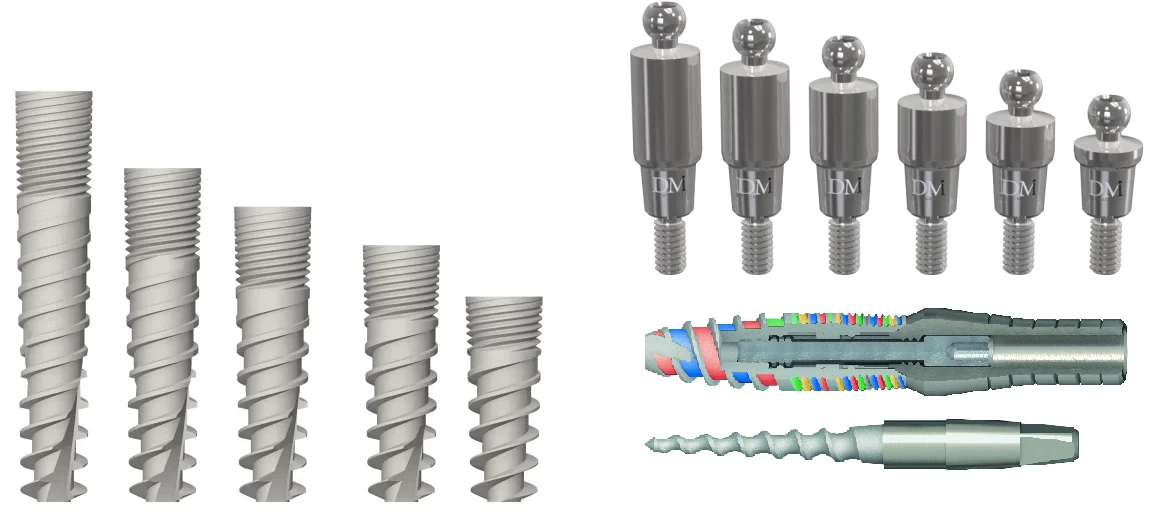
שתל דנטלי זהו שורש מלאכותי של השן, אשר מיוצר מטיטניום או חומר אחר התואם את גוף האדם.
השתלת שיניים – זה הליך כירורגי, שבזמנו השתל מוחדר לעצם הלסת. על השתל מורכב מבנה לשתל – סוג של מתאם. מעל מורכב הכתר, אשר תפקידו להחליף את השן, גם מבחינת נראות וגם מבחינה פונקציונאלית.
כך, שתלים דנטליים מהווים בסיס יציב לשיניים מלאכותיות.
ייעוץ ותכנון. לפני ההשתלה יש צורך בבדיקות נרחבות של עצם הלסת, שיניים סמוכות ומצב הבריאות הכללי.
הכנה. במקרים מסוימים יש צורך בבניית עצם (אוגמנטציה של העצם), במידה ואין מספיק עצם לביצוע ההשתלה.
התקנת השתל. תחת הרדמה, הרופא מתקין בזהירות את השתל בתוך העצם.
תהליך אוסטיאו-אינטגרציה. לאחר התקנת השתל, יתחיל תהליך איחוי השתל עם העצם, ורק לאחר מכן ניתן לעבור לשלב הבא.
התקנת המבנה לשתל והכתר. על השתל מורכבים מבנה לשתל והכתר הדנטלי.
אריכות ימים. תחזוקה נכונה של השתלים יכולה לשמור עליהם למשך כל החיים.
אסתטיקה. שיניים מלאכותיות נראות ומתפקדות כמו אמיתיות.
הגנה. השתלים עוזרים למנוע אטרופיה של עצם הלסת, המתרחשת כתוצאה מאובדן שיניים.
נוחות. שתלי שיניים לא מצריכים טיפול מיוחד או הורדה.
הטיפול בשתלי שיניים דומה לטיפול בשיניים טבעיות.
קיים צורך בהיגיינת פה שגרתית, כולל צחצוח שיניים פעמיים ביום ושימוש בחוט דנטלי.
כמו כן, נדרשים ביקורים סדירים אצל רופא השיניים לצורך מעקב וניקוי מקצועי.
שתלי שיניים בדרך כלל מיוצרים מחומרים התואמים ביולוגית, אשר מספקים אחיזה חזקה של השתל בתוך רקמת העצם.
החומרים העיקריים המשמים לייצור שתלים דנטליים הם:
טיטניום – החומר הנפוץ ביותר לייצור שתלי שיניים. חומר זה בעל תאימות ביולוגית גבוהה, ולא גורם לדחייה של השתל. טיטניום בעל תכונות מכאניות מעולות, המאפשרות לחזק את האחיזה בתוך העצם.
זירקוניה – בעל יציבות גבוהה ותאימות ביולוגית מעולה. כמו כן, בעל יתרון מבחינה אסתטית, בגלל צבעו הלבן. שתלים מזירקוניה יכולים לעלות יותר, ביחס לשתלים מטיטניום.
סגסוגות – שתלים מסוימים מיוצרים מסגסוגות שונות, כולל סגסוגות טיטניום.
שתלים מזירקוניה יותר קשיחים מאלו העשויים מטיטניום, אך פחות טובים מבחינת תכונות מכאניות. בהפעלת כוח מכאני משמעותי יכולים להישבר, לעומת אלה העשויים מטיטניום.
כמו כן, שתלים מזירקוניה נחקרים ונמצאים בשימוש פחות זמן.
תמיד יש לדון בנושא עם הכירורג המשתיל, כדי לבחור את חומר של השתלים בהתאם למצבכם המיוחד.
במידה ואתם חושבים על השתלת שיניים, חשוב מאוד להתייעץ עם רופא שיניים מומחה לקבלת תוכנית טיפולית והצעות מחיר.
איזה שתל דנטלי טוב יותר מחליט המומחה המשתיל.
שתלים דנטליים עכשוויים המיוצרים בשוויץ, ישראל, קוריאה או שוודיה, בעלי אחוזי קליטה גבוהים במיוחד – למעלה מ-91%-96%.
ההבדלים יכולים לבוא לידי ביטוי, בזמני הקליטה, תהליך אוסטיאו-אינטגרציה, אמינות ועלות הייצור.
בבחירת השתל, יש צורך לקחת בחשבון גם את חומר ממנו הוא מיוצר. לרוב, שתלי השיניים מיוצרים היום מטיטניום – חומר בטיחותי והיפואלרגני ביותר, שלא משפיע על הרקמות הסמוכות. אך לטובת קליטה מהירה היצרנים משתמשים בציפויים שונים. לדוגמה, הכי יוקרתי נחשב ציפוי תחמוצת טיטניום המועשר בפוספט.
מה שנוגע לעיצוב, ברוב המקרים האפשרות הטובה ביותר היא שתלים בצורת קונוס עם חריצים על פני השתל. צורה כזאת מאפשרת להאיץ את היווצרות קרמת העצם סביב השתל.
סוגי השתלים לפני צורת המבנה וטכנולוגיית ההתקנה:
בצורת שורש – הנפוצים ביותר, מתאימים לשימוש במקרים בהם ישנה רקמת עצם רבה.
בצורת טבליות – מתאימים במקרים בהם רקמת העצם אינה מספקת.
משולבים – בעלי צורה מורכבת ומתאימים לשימוש במקרים של ליקויים רציניים במערכת הלסתות והשיניים.
שתלים סאבפריאוסטליים – מיועדים למקרים קליניים עם רקמת עצם דקה.
שתלים מיוצבים מבחינה אנדודונטית – אלו שתלים העוזרים לרופאי שיניים להאריך ולחזק את שורש השן.
שתלים המותקנים בתוך רירית – לא מצריכים הברגה לתוך העצם, ומשמשים לטובת קיבוע תותבות.
השתלת שיניים - מאמרים ועצות עדכניות למטופלים בנושא השתלות שיניים, תותבות, עקירת שיניים ועוד.
ראה הכל


אנו נשלח הפניה לצילום רנטגן במייל שלך
(בדוק את דואר הספאם שלך)

ברכות! הפרטים נשלחו, המתינו להצעות מחיר
אתם מחפשים את
רופאי שיניים בקרבתכם?אתם צריכים הפניה
מאמרים שימושיים?אתם רוצים
לחשב את המחיר של טיפול השיניים שלכם?האם אתה מחפש
לצילום שיניים?